In the pursuit of a more sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle, solar energy has emerged as a frontrunner among renewable energy sources. One innovative way to harness this abundant power right at home is through solar balcony mounts. In this blog post, we'll explore what solar balcony mounts are, their numerous advantages, and how they can transform your living space into a clean energy - producing hub.
What are Solar Balcony Mounts?
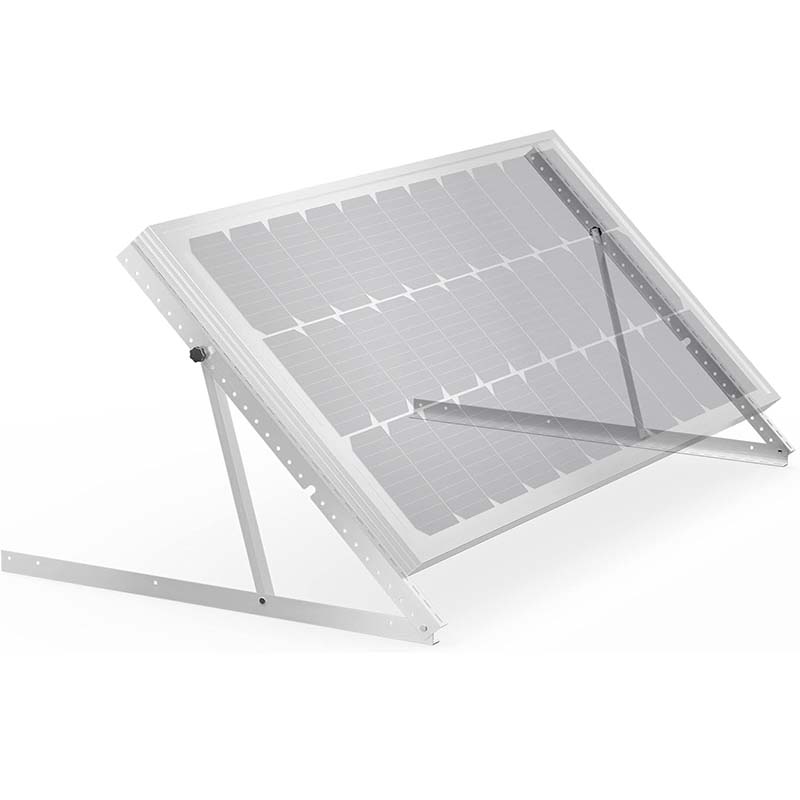
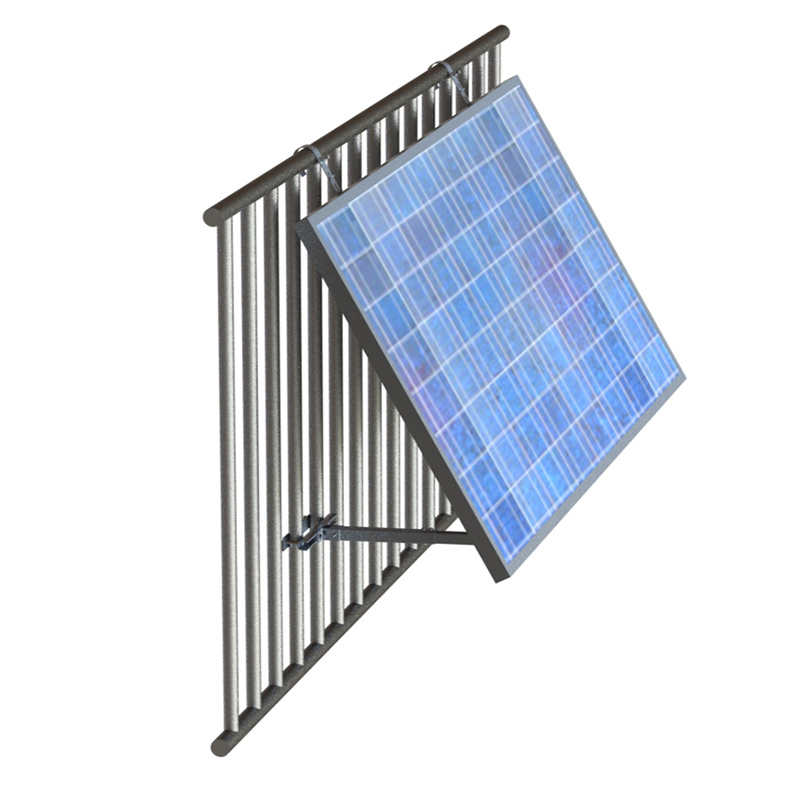
Solar balcony mounts are specialized structures designed to securely hold solar panels on balconies. They are a practical solution for those who may not have access to traditional roof - mounted solar installations, such as apartment dwellers, or for homeowners with limited or unsuitable roof space. These mounts are typically made from durable materials like high - strength aluminum alloy or stainless steel. They come in various designs, some with adjustable angles, allowing users to optimize the solar panels' exposure to sunlight throughout the day.
How Do They Work?
The installation of solar balcony mounts is relatively straightforward. The mount is first attached to the balcony railing, wall, or floor, depending on the design. Once the mount is securely in place, solar panels are then fixed onto it. The solar panels capture sunlight, which is composed of photons. These photons knock electrons loose from atoms in the solar panel's semiconductor material, creating an electric current. This direct current (DC) is then converted into alternating current (AC) through an inverter, which can be used to power household appliances and devices.
Advantages of Solar Balcony Mounts
Space - Saving Solution
Balconies are often under - utilized spaces. Solar balcony mounts allow you to make the most of this area without taking up additional land or roof space. This is especially beneficial in urban environments where space is at a premium. Whether you live in a small apartment or a house with a limited roof area, your balcony can now be transformed into a clean energy generator.
Cost - Effective Energy Generation
By installing solar panels on your balcony, you can generate your own electricity. This reduces your reliance on the grid, which in turn can lead to significant savings on your energy bills over time. As electricity prices continue to rise, having your own solar power source provides a degree of protection against these increases. Additionally, in some regions, there may be incentives or feed - in tariffs for generating your own renewable energy, further enhancing the cost - effectiveness of solar balcony mounts.
Environmental Benefits
Solar energy is a clean and renewable source of power. When you use solar balcony mounts to generate electricity, you are reducing your carbon footprint. Instead of relying on fossil - fuel - based energy sources that emit greenhouse gases, you are harnessing the sun's energy, which produces no harmful emissions during operation. This contributes to a cleaner environment and helps combat climate change.
Easy Installation
Many solar balcony mounts are designed for easy installation. They often come with pre - assembled components and detailed installation instructions, making it possible for homeowners to install them themselves, even without prior experience in solar installations. In cases where professional installation is preferred, the process is still relatively quick and straightforward compared to more complex solar projects, such as large - scale rooftop installations.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Solar balcony mounts are highly flexible. They can be adjusted to fit different balcony sizes, shapes, and orientations. Some mounts also allow for the adjustment of the solar panel angle, enabling you to optimize sunlight capture based on the time of day and the season. This adaptability ensures that you can make the most of the available sunlight, regardless of your balcony's specific characteristics.
Durability and Long - Lasting Performance
Constructed from high - quality materials like corrosion - resistant aluminum alloy or stainless steel, solar balcony mounts are built to withstand various weather conditions. They can endure strong winds, rain, snow, and exposure to sunlight without significant degradation. This durability means that once installed, they can provide reliable support for your solar panels for many years, often with a lifespan of 20 - 30 years or more.
Applications of Solar Balcony Mounts
Residential Use
In homes, solar balcony mounts can power a wide range of appliances, from lights and fans to small kitchen appliances. They can also be used to charge electric vehicles (if the system is sized appropriately). This not only saves money but also gives homeowners a sense of energy independence.
Urban Buildings
High - rise apartment buildings, condominiums, and even commercial buildings in urban areas can benefit from solar balcony mounts. By installing solar panels on balconies, these buildings can reduce their overall energy consumption and contribute to a more sustainable urban environment. Some building owners may also be able to offset a portion of their electricity costs, making it a financially viable option.
Off - Grid or Remote Locations
For those living in remote cabins, campsites, or areas with limited or unreliable grid access, solar balcony mounts can be a reliable source of power. They can provide electricity for basic needs such as lighting, charging devices, and running small appliances, making off - grid living more comfortable and sustainable.
In conclusion, solar balcony mounts offer a practical, cost - effective, and environmentally friendly way to harness solar energy. Whether you're looking to save money on your energy bills, reduce your carbon footprint, or simply make use of an under - utilized space, solar balcony mounts are definitely worth considering. So, why not take the first step towards a greener future and explore the possibilities of installing solar balcony mounts on your own balcony today?
Read More




























 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported
